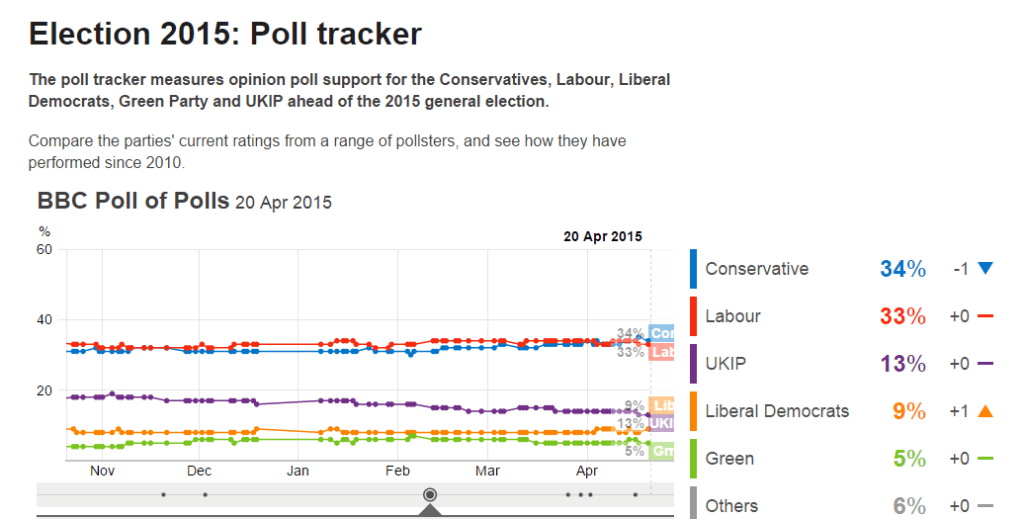
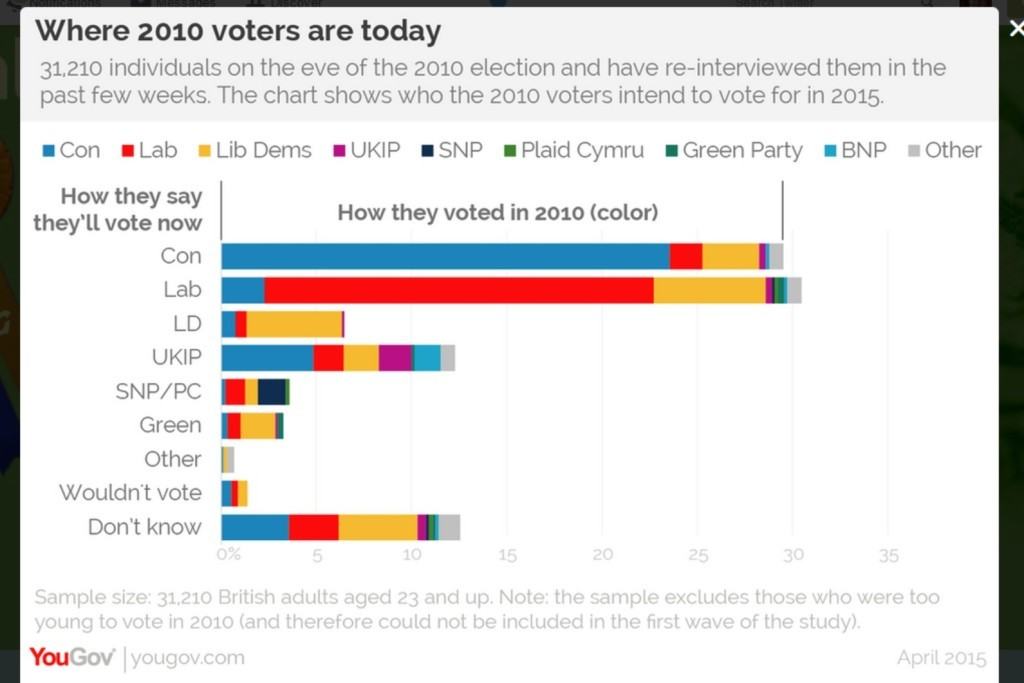
After the economy the biggest issue in Britain’s General Election is the NHS. This comes top, or near to the top, of most voters’ lists of concerns. Labour want to make the most of these worries, while the Conservatives want to muddy the waters.
Two things seem to worry voters in particular. The first is pressure on Accident & Emergency services, which is knocking on to other parts of the system. This gives a general sense of the system failing. The second is the effect of NHS reorganisations of local services. This is often associated with outsourcing. Whether the public is as incensed about this “privatisation” as people on the left think is an interesting question – but they are suspicious of any threat to familiar local services.
That the NHS is under stress should be no surprise. As the proportion of older people in the population rises, so does the workload – but not the tax base from which it is funded. Furthermore many new treatments tend to be expensive; technological change does not improve productivity – but simply increases demand as new treatments are found.
There is political consensus around the free-at-the-point of use principle of the NHS. This has both flaws and strengths, but the NHS does quite well in international comparisons, though more for value for money than keeping people alive. Given this there are two important issues for the politicians to tackle. The first is organisational architecture, and the second is funding. They are related, of course, since the efficiency with which the service uses its funding depends on the architecture of the service. But it helps to keep the two separate for now.
First let’s consider this organisational architecture. The NHS has evolved since a chaotic mix of institutions was nationalised in the 1940s. Two ideas have always competed: a Soviet-style command and control model, with clear accountability to the politician at the top of the system; or a demand led organisation where users create demand and the service is forced to follow it. The Left tends to focus on the first, which is slow to react to change, and beset by tribal organisational silos. The Right prefers the latter, which suffers from a lack of reliable information about the true level of demand, and creates organisational instability.
What we have is a compromise between the two approaches. The service is divided between commissioners, who identify what services are needed and make choices as what to prioritise with the available money. And providers, such as hospitals, who actually deliver services based on the identified demand, a small proprtion of which is outsourced to the private sector. In addition there are other organisations charged with making it all work, including regulators of various sorts. This includes NICE, which rules on what treatments provide acceptable value for money. This basic architecture was established by the last Labour government, and remains largely unchallenged by the parties – though it is disliked by many health professionals.
But the details of Labour’s system were flawed. It was designed by management consultants in less stringent times. At its heart was an over-engineered monster called World Class Commissioning, with commissioning being spread out amongst a large number of Primary Care Trusts – which were bureaucratic, with little clinical input and token local accountability. The Coalition rightly attacked this structure, and set about redesigning it – with commissioning now being given to a combination of national specialist bodies and local commissioning groups, run by general practitioners. This succeeded both in bringing in more clinical input and improved local accountability. But it was a massive and distracting exercise (in spite of a Tory promise of “no top-down reorganisations”, enshrined in the coalition agreement). This was a serious mistake which has left much muddle in its wake. It was perfectly possible to achieve much the same ends on an evolutionary basis – piloting different approaches in different regions. The reorganisation has created a huge amount of bad blood, and not a little paranoia amongst health professionals. It has been accompanied by a steady process of outsourcing elements of the service, though no private or third sector organisation will take on the major hospitals that are at the system’s heart.
Alongside this reorganisation has been steadily increasing demand, which has run ahead of funding. The combination has resulted in huge organisational stress. The way in which the service started to cope with the extra demand, and the need for greater efficiency, was classic top-down and Labour-inspired. It was called the “Nicholson challenge” after the then Chief Executive of England’s NHS. Funds were ratcheted down gradually each year on all parts of the system, with a bullying “just-do-it” approach. This did not unlock enough of the creative thinking and deeper re-engineering that the service required. Much of the result was mindless cutting and hoping for the best. Under a new Chief Executive (with reduced job scope), Simon Stevens, a more intelligent approach is being adopted – but the wreckage remains.
Given this history, surely the best idea is to work on the current structure on an evolutionary basis. This is what the coalition parties propose to do. The main work-in-progress is something called “integration”. This means getting social care, run by local authorities, to run jointly with the NHS. Awkwardly, this cuts across many of the bureaucratic structures currently in place, especially when it comes to parcelling up the money. It is far from straightforward, and it makes sense to proceed by means of locally run pilot schemes. It runs alongside greater devolution of responsibilities, as exemplified by the recent deal regarding Greater Manchester. The wider the scope of a service, the more localised the organisation has to be in order to prevent unmanageable complexity and stasis.
The main challenge for Conservatives is their approach to outsourcing. There is nothing wrong with outsourcing elements of the NHS. It can bring in fresh ideas and fresh management. It can be used to bring in new ownership structures, like cooperatives and social enterprises, to replace the hierarchical empires that the current NHS fosters. But the way it has worked out is dysfunctional. The tendering process can be so complicated that only behemoth suppliers need apply. These behemoths can afford slick tenders put together by professional marketers and priced at whatever level it takes to win. Once they win they are free to break their promises and a general period of mindless hollowing out follows. Sometimes this is what is needed; usually not. Many Conservatives just don’t get this.
The challenge to Labour is a bigger one. They want to respond to the anger over the last reorganisation and reverse parts of it. Does this imply another chaotic reorganisation? Will it kill the good elements of reforms along with the bad? Do they think integration should be enforced top-down from the centre? Or will they follow the path of devolving political responsibilities? Does their idea of in-house NHS services being given preference mean less value for money and slower innovation? Will their idea of capping the profits of the outsources prove to be yet more bureaucracy that favours the heartless behemoths rather than the innovative social enterprises? Will Labour revert to the top-down, bullying style of management of old? And will they need SNP votes to get their reforms to the English system through? More uncertainty and chaos beckons.
The Lib Dems have a rather interesting take on NHS policy. They want to prioritise mental health services. As I have written elsewhere, I think this approach is inspired, and one of the better reasons for voting for the party. They stand for intelligent continuity.
And so we come to funding. Britons do not spend a particularly high level of money on health services (much less proportionately than the Americans), and there is no economic reason why the country shouldn’t spend a lot more than it does. There is no evidence that the overall level of demand is excessive because the service is free; people really want the services, and would pay a lot for it them if they had to. The problem is the opposite: funding is constrained by the need to pay for the service through taxes, where it competes with a whole lot of other things, like schools and policemen. And the government isn’t raising anything like enough tax to pay for it all.
Last year Mr Stevens produced a plan which showed that the service will need an extra £8bn per annum in five years’ time, even after a lot of efficiency savings. Will the political parties follow his plan? The problem is that its affordability depends on how well the economy and the tax base does – which is unknowable. The gaps between the parties come down to the different ways in which they are handling these forecasting uncertainties. The Conservatives are the most optimistic, Labour the least, and the Lib Dems somewhere in between. None of them are committing to sufficient tax rises if a growing economy does not deliver the extra tax revenue. Both Labour and the Lib Dems are offering some tax gimmicks to help close the gap, but none are offering the increases to Income Tax, VAT or National Insurance that will be required if the economists get their growth projections wrong (yet again). Labours plans are obscured by their issues of NHS organisation; they will not sign up to Mr Stevens’s plan for that reason.
If the NHS is starved of funds more people will go private, social solidarity will fade and a death spiral will be put in motion. Something very like this has happened to NHS dentistry. If we want to keep the NHS in its current format, with few charges, then this means extra tax, and not just the somebody-else-is-paying sort. It really is quite simple. It is very disappointing that our politicians (and Ukip, the Greens and the SNP are as bad as the others, or worse) will not face up to this. I find it impossible to choose between the parties based on their funding proposals.
Which leaves organisation as being the decisive issue. The coalition managed one step forward and one back. Labour’s attitude to organisation threatens another step or two backwards. The Conservatives are suspect on outsourcing and the most suspect on funding. The Lib Dems offer intelligent continuity, but, sadly, even in coalition they are unlikely to be given enough scope to put their way forward into practice.